CDS is a fundamental part of RAP development
Core Data Services (CDS) are a central and fundamental factor in ABAP RESTful Application Programming (RAP) development, forming the basis of any application, especially within SAP S/4HANA and the SAP Cloud Platform ABAP Environment. They are considered one of the key technologies in the ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model.
The importance of CDS in RAP
Here are the key factors highlighting the importance of CDS in RAP development:
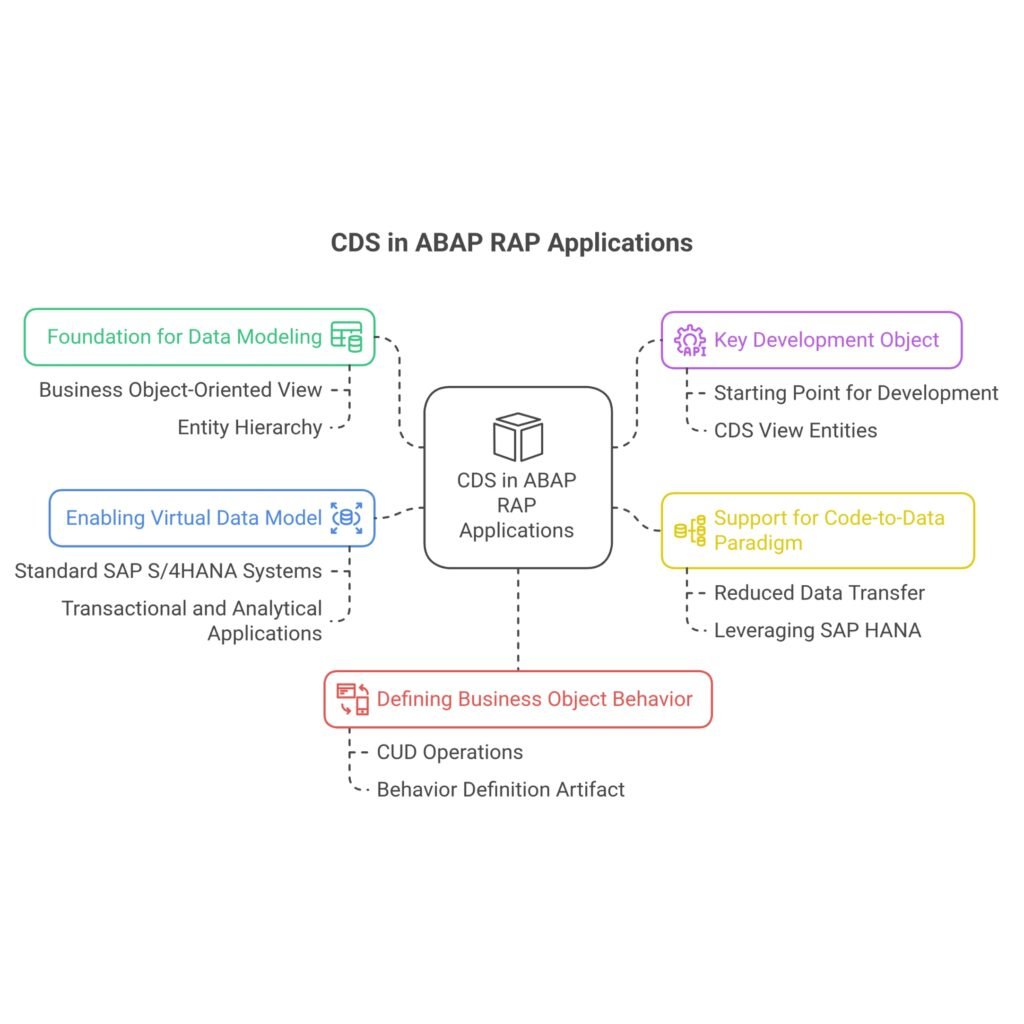
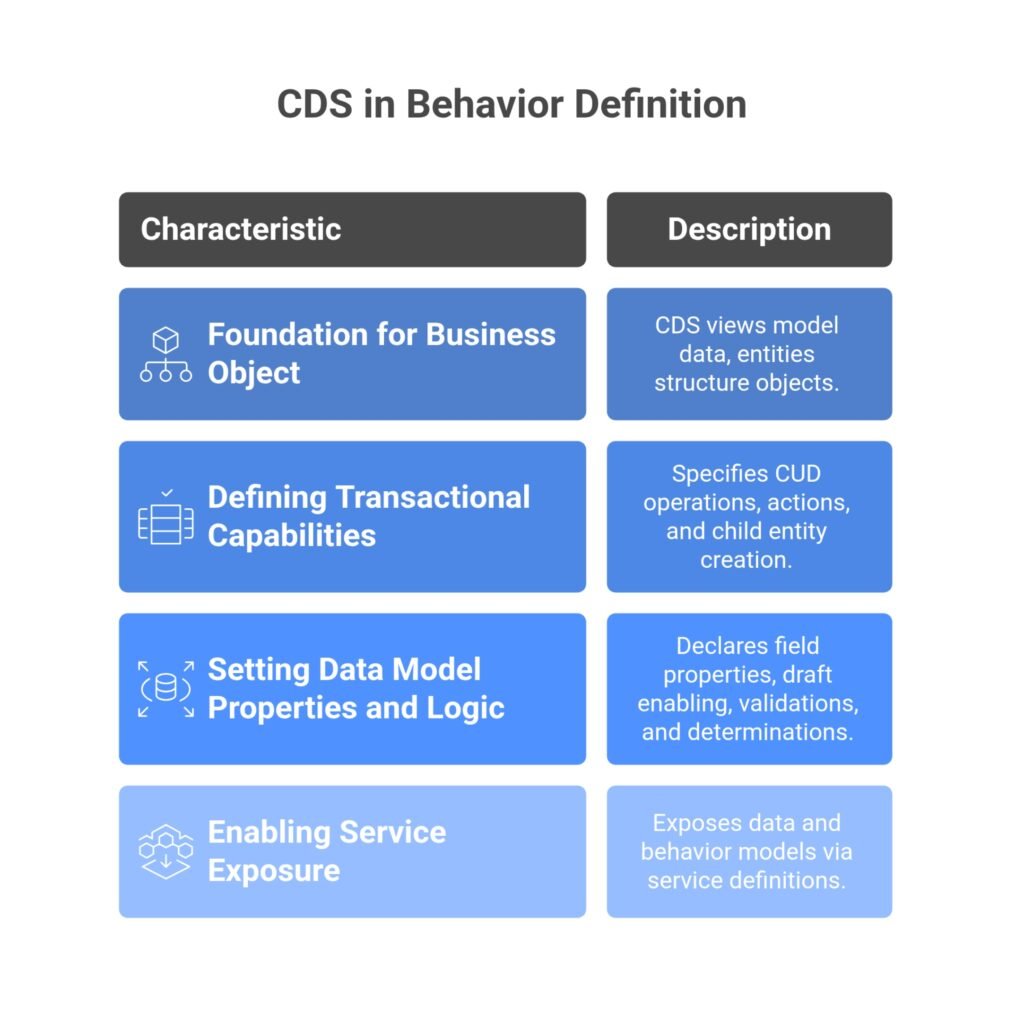
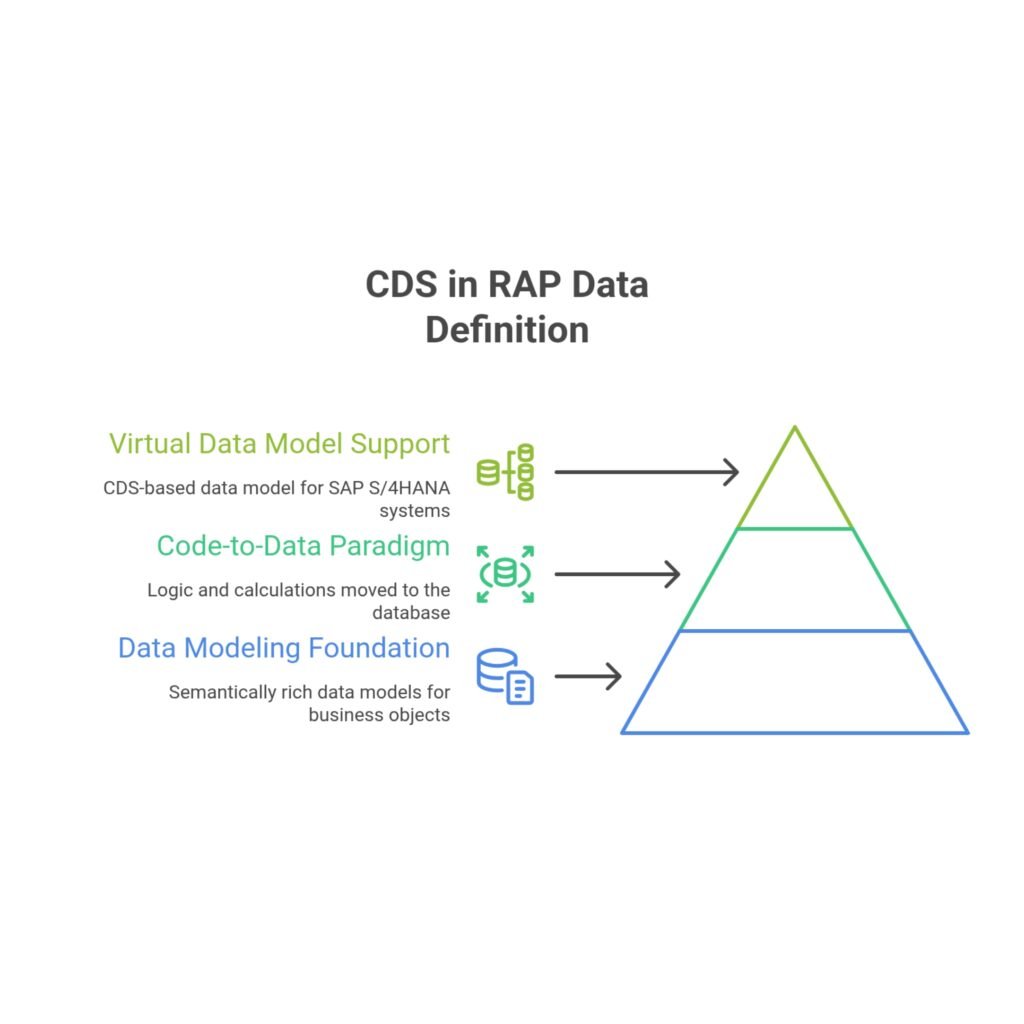
- Foundation for Data Modeling: CDS provides an infrastructure for developers to create semantically rich and persistent data models. These models are built on existing database tables but offer a business object-oriented view of data, moving away from a purely technical perspective of database tables. They are the central tool for data modeling in RAP.
- Key Development Object: CDS entities (specifically CDS view entities) are a core development object in RAP applications. They are the starting point for developing RAP applications, typically after defining database tables.
- Support for the Code-to-Data Paradigm: CDS views are excellently suited for implementing the code-to-data paradigm. This paradigm aims to move application logic from the application server to the database, allowing the database system to perform calculations and access controls directly within the data model. This approach reduces data transfer and leverages the power of the SAP HANA database.
- Enabling the Virtual Data Model (VDM): CDS serves as a tool for data modeling within SAP’s Virtual Data Model (VDM). The VDM is a data model based on CDS provided in standard SAP S/4HANA systems, used by transactional and analytical applications and APIs. It acts as an additional data access layer for SAP S/4HANA developers.
- Defining Business Object Behavior: Every entity within a business object can offer standard Create, Update, Delete (CUD) operations, as well as specific actions. These operations, along with behavior-relevant properties like lock dependencies, are defined in a behavior definition artifact.
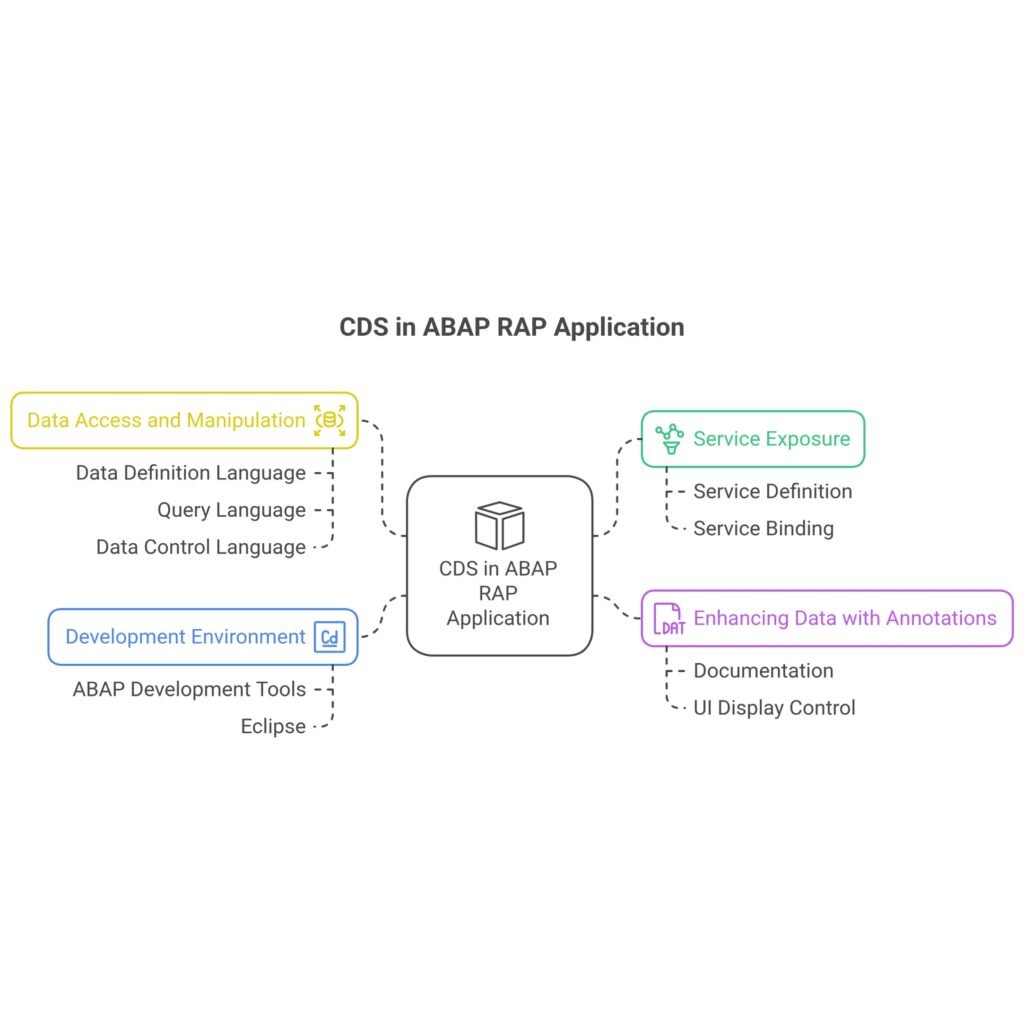
- Service Exposure: In RAP, a business service is defined by exposing data models and behavior models. The Service Definition is a projection of the underlying CDS-based data model and related behavior to be exposed.
- Enhancing Data with Annotations: These annotations can be used for documentation purposes, to activate certain functions, and can be evaluated by consumers of the data model. Examples include defining translatable texts, controlling UI display, classifying views for the VDM, providing semantic information, and managing access control.
- Data Access and Manipulation: CDS views are used for flexible data retrieval. They include domain-specific languages like Data Definition Language (DDL) for modeling, Query Language (QL) for querying, and Data Control Language (DCL) for access restrictions. CDS views can be called from within ABAP programs using SELECT statements, similar to database tables. They can also be called from other CDS views, enabling a hierarchical structure of CDS-based data models (view stack).
- Development Environment: Working with CDS views necessitates the use of ABAP Development Tools (ADT) in Eclipse. ADT provides tools like data preview, SQL console, and language references to assist in CDS development and analysis.
In summary, CDS is not merely a data modeling tool but an integral part of the entire RAP development lifecycle, from defining the data structure and behavior to exposing services and ensuring data security and performance